Installing compilers
As your Puppet Enterprise infrastructure scales up to 4,000 nodes and beyond, add load-balanced compilers to your installation to increase the number of agents you can manage.
Each compiler increases capacity by 1,500 to 3,000 nodes, until you exhaust the capacity of PuppetDB or the console.
How compilers work
A single primary server can process requests and compile code for up to 4,000 nodes. When you exceed this scale, expand your infrastructure by adding compilers to share the workload and compile catalogs faster.
https://<hostname>:8140/status/v1/simple.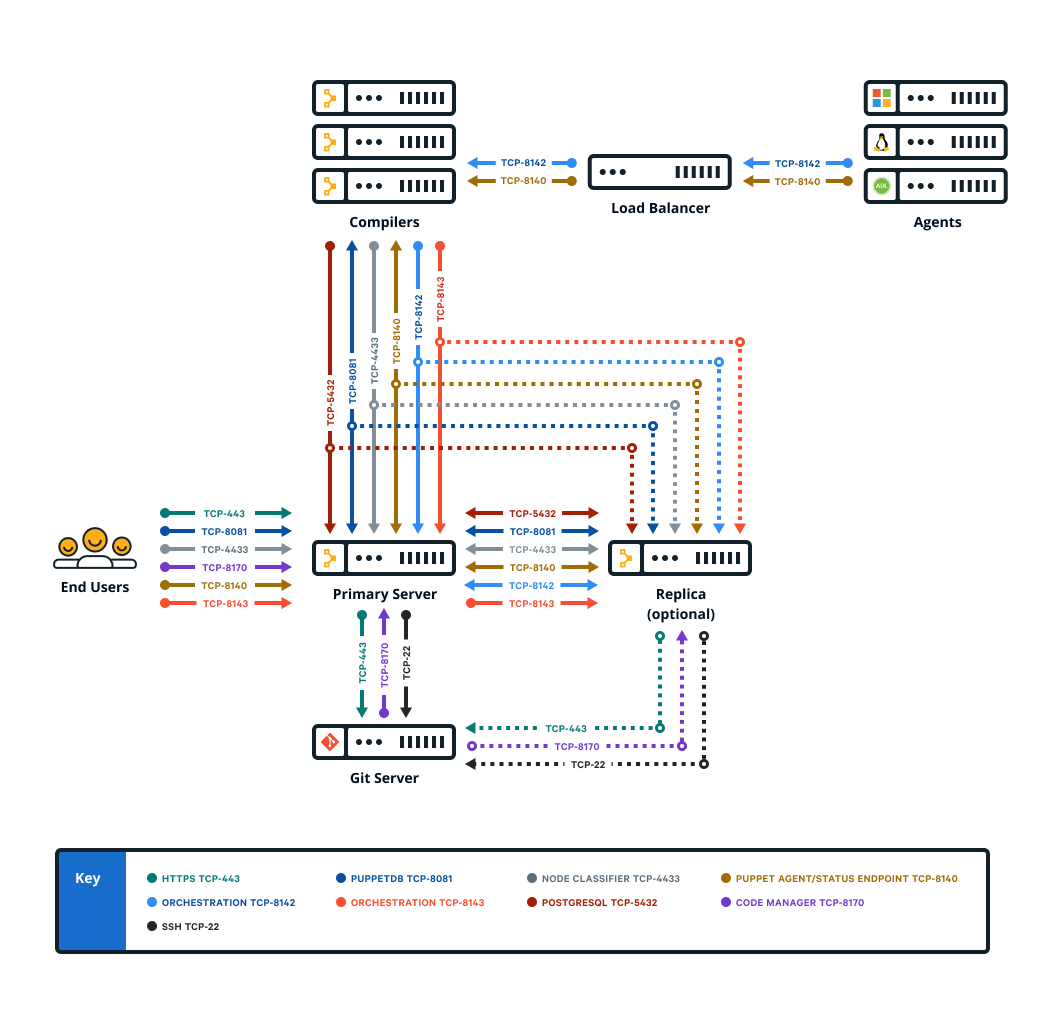
Components and services running on compilers
Compilers typically run Puppet Server and PuppetDB services, as well as a file sync client. Older, legacy-style compilers must be converted in order to add PuppetDB.
When triggered by a web endpoint, file sync takes changes from the working directory on the primary server and deploys the code to a live code directory. File sync then deploys that code to all your compilers. By default, compilers check for code updates every five seconds.
The certificate authority (CA) service is disabled on compilers. A proxy service running on the compiler Puppet Server directs CA requests to the primary server, which hosts the CA in default installations.
Compilers also have:
- The repository for agent installation,
pe_repo - The controller profile used with PE client tools
- Puppet Communications Protocol (PCP) brokers to enable orchestrator scale
Logs for compilers are located at
/var/log/puppetlabs/puppetserver/.
Logs for PCP brokers on compilers are located at
/var/log/puppetlabs/puppetserver/pcp-broker.log. Logback
configuration for PCP broker logs is part of the Orchestration services settings.
Using load balancers with compilers
When using more than one compiler, a load balancer can help distribute the load between the compilers and provide a level of redundancy.
Specifics on how to configure a load balancer infrastructure falls outside the scope of
this document, but examples of how to leverage haproxy for this purpose
can be found on the HAproxy module Forge
page.
Calculating load balancing
PCP brokers run on compilers and connect to PXP agents over port 8142. PCP brokers are built on websockets and require many
persistent connections. If you're not using HTTP health checks, we recommend using a
round robin or random load balancing algorithm for PXP agent connections to PCP brokers, because PCP brokers don't operate independent of the
orchestrator and isolate themselves if they become disconnected. You can check
connections with the /status/v1/simple endpoint for an error state.
Configure your load balancer to avoid closing long-lived connections that have little
traffic. In the HAproxy module, you can set the timeout tunnel to
6m because PCP brokers
disconnect inactive connections after 6 minutes. You can also configure the idle-timeout in the PCP broker trapperkeeper service configuration part of your Orchestration services settings.
Due to the diverse nature of the network communications between the agent and the primary server, we recommend that you implement a load balancing algorithm that distributes traffic between compilers based on the number of open connections. Load balancers often refer to this strategy as "balancing by least connections."
Using health checks
The Puppet REST API exposes a status endpoint that can be leveraged from a load balancer health check to ensure that unhealthy hosts do not receive agent requests from the load balancer.
The primary server service responds to unauthenticated HTTP GET requests issued to
https://<hostname>:8140/status/v1/simple. The API
responds with an HTTP 200 status code if the service is healthy.
If your load balancer doesn't support HTTP health checks, a simpler alternative is to check that the host is listening for TCP connections on port 8140. This ensures that requests aren't forwarded to an unreachable instance of the primary server, but it does not guarantee that a host is pulled out of rotation if it's deemed unhealthy, or if the service listening on port 8140 is not a service related to Puppet.
Load balancing for multi-region installations
If you have load balancers in multiple regions, use a global DNS proximity-based service address.
When using a centralized Puppet deployment with multiple regional proxies or load balancers, create a global DNS proximity-based service address for Puppet and use that to route agents to the appropriate regional load balancer based on their location. Set the global DNS proximity-based address as the compiler pool address in Hiera.
pe_repo::compile_master_pool_address: "<PUPPET-GLOBAL-SERVICE-ADDRESS>"- BIG-IP DNS
- Route 53 Geolocation routing in AWS
- TCP Proxy Global Load Balancing in GCP
- Traffic Manager in Azure
Install compilers
Installing a compiler adds the specified node to the PE Infrastructure Agent and PE Compiler node groups and installs the PuppetDB service on the node.
To install a FIPS-compliant compiler, install the compiler on a supported platform with FIPS mode enabled. The node must be configured with sufficient available entropy or the installation process fails.
Configure compilers
Compilers must be configured to appropriately route communication between your primary server and agent nodes.
Install compilers and load balancers.
If you need DNS altnames for your load balancers, add them to the primary server.
Ensure port 8143 is open on the primary server or on any workstations used to run orchestrator jobs.
Convert existing compilers
If you have legacy compilers, you can improve their usability and scalability by adding PuppetDB. In addition to installing the PuppetDB service, converting an existing compiler adds the node to the PE Compiler node group and unpins it from the PE Master node group.
puppet infrastructure run convert_legacy_compiler compiler=<COMPILER_FQDN-1>,<COMPILER_FQDN-2>puppet infrastructure run convert_legacy_compiler all=truepuppet infrastructure tune on your primary
server and adjust tuning for compilers as needed.